Harvard Architecture is the computer architecture that contains separate storage and separate buses (signal path) for instruction and data. It was basically developed to overcome the bottleneck of Von Neumann Architecture. The main advantage of having separate buses for instruction and data is that the CPU can access instructions and read/write data at the same time.
Structure of Harvard Architecture:
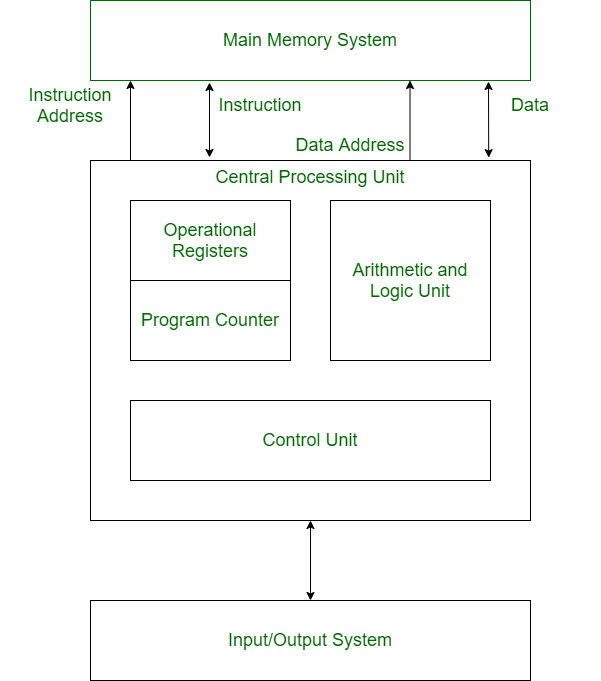
Structure of Harvard Architecture
Buses
Buses are used as signal pathways. In Harvard architecture, there are separate buses for both instruction and data. Types of Buses:
- Data Bus: It carries data among the main memory system, processor, and I/O devices.
- Data Address Bus: It carries the address of data from the processor to the main memory system.
- Instruction Bus: It carries instructions among the main memory system, processor, and I/O devices.
- Instruction Address Bus: It carries the address of instructions from the processor to the main memory system.
Operational Registers
There are different types of registers involved in it which are used for storing addresses of different types of instructions.
For example, the Memory Address Register and Memory Data Register are operational registers.
Program Counter
It has the location of the next instruction to be executed. The program counter then passes this next address to the memory address register.
Arithmetic and Logic Unit
The arithmetic logic unit is that part of the CPU that operates all the calculations needed. It performs addition, subtraction, comparison, logical Operations, bit Shifting Operations, and various arithmetic operations.
Control Unit
The Control Unit is the part of the CPU that operates all processor control signals. It controls the input and output devices and also controls the movement of instructions and data within the system.
Input/Output System
Input devices are used to read data into main memory with the help of CPU input instruction. The information from a computer as output is given through Output devices. The computer gives the results of computation with the help of output devices.
Advantage of Harvard Architecture:
Harvard architecture has two separate buses for instruction and data. Hence, the CPU can access instructions and read/write data at the same time. This is the major advantage of Harvard architecture.
In practice, Modified Harvard Architecture is used where we have two separate caches (data and instruction). This is common and used in X86 and ARM processors.